Acute Wilsonian Hepatitis And Fulminant Wilson Disease
Published on September 19 2014
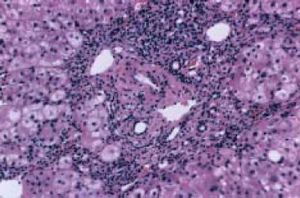
Acute Wilsonian hepatitis is indistinguishable from other forms of acute (viral or toxic) liver diseases. It should be suspected in young patients with acute non-viral hepatitis. Liver histology often reveals the presence of cirrhosis.
This initial episode of liver damage may be self-limiting and may resolve without treatment, and diagnosis is made retrospectively, when neurologic symptoms occur years later.
On the other hand the disease may rapidly deteriorate and resemble fulminant hepatic failure with massive jaundice, hypoalbuminemia, ascites, severe coagulation defects, hyper-ammonemia and hepatic encephalopathy. Hepatocellular necrosis results in the release of large amounts of stored copper. Hypercupremia results in hemolysis and severe hemolytic anemia complicates acute liver disease.
Although Wilson disease is rare, in patients presenting with fulminant hepatic failure it is not uncommon and accounts for 6-12% of patients with fulminant hepatic failure referred for emergency liver transplantation.
Although fulminant and subfulminant liver failure http://livertox.nih.gov/Phenotypes_fail.html due to Wilson disease has several distinctive features, rapid diagnosis may be very difficult. Serum aminotransferase activity is usually not increased above 10 times normal and thus the levels are much lower than the levels commonly recorded in fulminant hepatitis. The combination of anemia, marked jaundice and relatively low aminotransferase activities in young patients should always raise the suspicion of acute Wilson disease.
The conventionally-used parameters of copper metabolism are of little use. Kayser-Fleischer corneal rings and neurologic abnormalities are absent in most patients presenting with acute liver disease. An alkaline phosphatase-total bilirubin ratio below 2.0 has been claimed to provide 100% sensitivity and specificity to diagnose Wilsonian fulminant liver failure, but the usefulness of this test has not been confirmed in larger series.
The best diagnostic test is the quantification of copper in biopsy material or in the explanted liver. One puzzling feature of fulminant Wilson disease is the preponderance of the female sex (female:male ratio 3:1).
/image%2F1207985%2F20140911%2Fob_a8710a_1.jpg)
/image%2F1207985%2F20140911%2Fob_a4ffc4_header-03.jpg)